
Copper coils are found in many everyday devices—from transformers and electric motors to wireless chargers and generators. But how exactly does a copper coil work? In this blog, we’ll explore the basic principles behind copper coils, including electromagnetism, electromagnetic induction, and their real-world applications.
A copper coil, often called a solenoid when wound in loops, is simply copper wire wound into a spiral or cylindrical shape. Copper is used because it has low electrical resistance and excellent conductivity, making it ideal for carrying electric current.
There are two primary scientific principles that explain how a copper coil works:
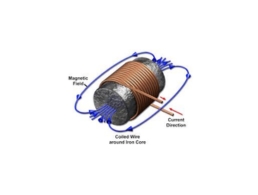
When an electric current passes through a copper coil, it generates a magnetic field around the coil. This is described by Ampère’s Law, which states that magnetic fields are produced by electric currents.
The magnetic field is stronger with:
More loops in the coil
Higher current
A ferromagnetic core (like iron)
Electromagnets
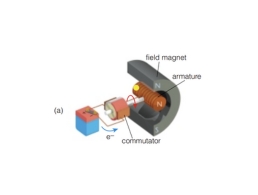
Electric motors
Solenoids
When the magnetic field around a copper coil changes—either by moving a magnet near the coil or changing the magnetic field strength—a voltage (or EMF) is induced in the coil. This is governed by Faraday’s Law of Induction.
The induced voltage is stronger with:
More turns in the coil
Faster change in magnetic field
Stronger magnets
Generators
Inductive sensors
Wireless charging
Copper is the preferred material for coils because it has:
Low electrical resistance → minimal energy loss
High conductivity → efficient current flow
Ductility → easily wound into coils
Copper coils are used in a wide range of electrical and electronic devices:
| Application | How the Copper Coil Works |
|---|---|
| Transformers | Transfer electricity between circuits using magnetic induction |
| Electric Motors | Convert electrical energy into mechanical motion |
| Generators | Convert mechanical motion into electrical energy |
| Wireless Chargers | Induce current wirelessly through changing magnetic fields |
| Metal Detectors | Detect metallic objects by sensing disruptions in magnetic fields |
Copper coils are vital components in modern electrical engineering. Whether creating a magnetic field by passing current through them or generating voltage via changing magnetic fields, they are key to countless technologies.
Understanding how they work not only deepens our knowledge of physics but also opens doors to innovations in energy, automation, and wireless technologies.
Q1: What is a copper coil?
A copper coil is a wire made of copper that is wound into a spiral or loop. It’s commonly used in electrical devices to create magnetic fields or generate electricity.
Q2: Why is copper used for coils?
Copper is used because it conducts electricity very well and has low resistance. This means it allows electricity to flow easily with minimal energy loss.
Q3: How does a copper coil create a magnetic field?
When electric current flows through the coil, it generates a magnetic field around it. The more loops in the coil, the stronger the magnetic field.
On Orders AED 5000.
Support online 24 hours a day
View our benefits.
Payment methods.
Order on WhatsApp.
Copyright 2024 © AL RAMIZ. All right reserved. Irfan Ullah